Detection of swallowing and breathing using an in-ear microphone
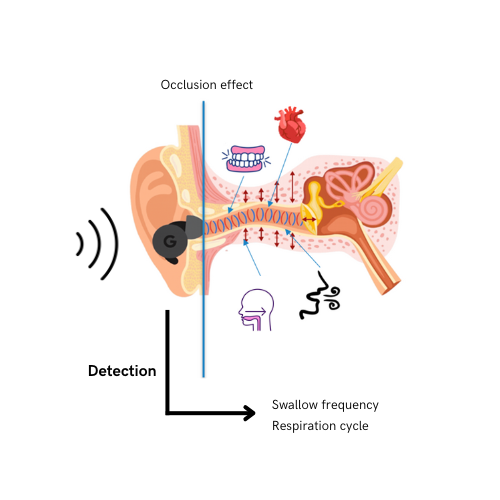
In health monitoring, using in-ear microphones can identify sound patterns indicating coordination issues between swallowing and breathing, crucial for conditions like sialorrhea for people with Parkinson's disease. By detecting the frequency of swallowing and the timing of the respiratory cycle, we can potentially verify the hypothesis that excessive drooling in people with Parkinson's disease is due to impaired swallowing rather than excessive saliva production. To achieve this, ultrasound serves as a control method to distinguish spontaneous and food swallowing from other activities to have a labeled dataset for a machine learning algorithm.
